AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service: running ALB Ingress controller
AWS ALB Ingress Controller for Kubernetes — is a Kubernetes controller which actually controls AWS Application Load Balancers (ALB) in an…
AWS ALB Ingress Controller for Kubernetes — is a Kubernetes controller which actually controls AWS Application Load Balancers (ALB) in an AWS account when an Ingress resource with the kubernetes.io/ingress.class: alb annotation is created in a Kubernetes cluster.
This Ingress resource in its turn describes an ALB Listeners configuration with SSL termination or traffic routing to the cluster's WorkerNodes.
More in the documentation here:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/ingress/
https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-alb-ingress-controller
https://aws.amazon.com/ru/blogs/opensource/kubernetes-ingress-aws-alb-ingress-controller/
Ingress controller types
AWS ALB Ingress controller supports two policy types for traffic routing — the instance mode and the ip mode:
instance mode: traffic will be accepted on an ALB, then routed to a NodePort Service, then routed to pods inside of the cluster
ip mode: traffic will go to an ALB first, then is routed directly to pods in a cluster. The documentation states that it’s necessary to install the AWS CNI plugin for Kubernetes, but in AWS EKS it works out of the box
See more documentation here>>>.
eksctl - create a cluster
At first, let’s create a testing cluster:
$ eksctl create cluster — profile arseniy — region eu-north-1 — name eks-alb-testing
[ℹ] eksctl version 0.15.0
[ℹ] using region eu-north-1
[ℹ] setting availability zones to [eu-north-1b eu-north-1c eu-north-1a]
[ℹ] subnets for eu-north-1b — public:192.168.0.0/19 private:192.168.96.0/19
[ℹ] subnets for eu-north-1c — public:192.168.32.0/19 private:192.168.128.0/19
[ℹ] subnets for eu-north-1a — public:192.168.64.0/19 private:192.168.160.0/19
[ℹ] nodegroup “ng-c408bab3” will use “ami-0d40170cbe0b51e62” [AmazonLinux2/1.14]
[ℹ] using Kubernetes version 1.14
[ℹ] creating EKS cluster “eks-alb-testing” in “eu-north-1” region with un-managed nodes
…
[ℹ] node “ip-192–168–11–166.eu-north-1.compute.internal” is ready
[ℹ] node “ip-192–168–35–128.eu-north-1.compute.internal” is ready
[ℹ] kubectl command should work with “/home/setevoy/.kube/config”, try ‘kubectl get nodes’
[✔] EKS cluster “eks-alb-testing” in “eu-north-1” region is readyIAM OIDC provider
Documentation — https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/enable-iam-roles-for-service-accounts.html.
The OIDC integration is necessary for the ServiceAccount used for the Controller, see more at https://eksctl.io/usage/iamserviceaccounts.
Create it:
$ eksctl — profile arseniy — region=eu-north-1 utils associate-iam-oidc-provider — cluster eks-alb-testing — approve
[ℹ] eksctl version 0.15.0
[ℹ] using region eu-north-1
[ℹ] will create IAM Open ID Connect provider for cluster “eks-alb-testing” in “eu-north-1”
[✔] created IAM Open ID Connect provider for cluster “eks-alb-testing” in “eu-north-1”Check:
$ aws — profile arseniy. — region=eu-north-1 eks describe-cluster — name eks-alb-testing — query “cluster.identity.oidc.issuer” — output text
https://oidc.eks.eu-north-1.amazonaws.com/id/B59F43D7826EB61861FC73EE13216CD8Or via AWS UI > Identity providers:
ALB IAM policy
The next step is to add an IAM policy that will give access for a pod with the ALB Ingress Controller in an AWS Account to make an API-calls to the AWS Core to create and configure Application Load Balancers.
It can be created using AWS CLI with the following command:
$ aws — profile arseniy — region=eu-north-1 iam create-policy — policy-name ALBIngressControllerIAMPolicy — policy-document https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-alb-ingress-controller/v1.1.4/docs/examples/iam-policy.jsonOr can be added to a CloudFormation template using the AWS::IAM::Role resource.
In the command’s output you’ll have an ARN — “Arn”: “arn:aws:iam::534***385:policy/ALBIngressControllerIAMPolicy” — keep it, we will use it in the following step.
ALB Ingress IAM Role
See https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-service-account/
1 iamserviceaccount (kube-system/alb-ingress-controller) was excluded
In the official documentation, the order is a bit different: first, it suggests to create an RBAC-role and RoleBinding, and after that — iamserviceaccount.
In my case, this led to the error during creating a new ServiceAccount “kube-system/alb-ingress-controller” — eksctl told that it is already present and skips it despite the --override-existing-serviceaccounts option:
[ℹ] eksctl version 0.15.0
[ℹ] using region eu-north-1
[ℹ] 1 iamserviceaccount(s) that already exist (kube-system/alb-ingress-controller) will be excluded
[ℹ] combined exclude rules: kube-system/alb-ingress-controller
[ℹ] 1 iamserviceaccount (kube-system/alb-ingress-controller) was excluded (based on the include/exclude rules)
[!] serviceaccounts that exists in Kubernetes will be excluded, use — override-existing-serviceaccounts to override
[ℹ] no tasksAfter containing AWS SUpport (love these guys — the best support overall Cloud providers, in my opinion) we’ve changed the order: first, create the IAM-role, and after that — RBAC Role and binding.
But — let’s go ahead.
Check the currently configured cluster — just in case:
$ kubectl config current-context
arseniy@eks-alb-testing.eu-north-1.eksctl.ioOkay.
Now create the IAM role using the eksctl, and using the ARN of the policy created above - attach it to this role (will create an additional CloudFormation stack):
$ eksctl — profile arseniy — region=eu-north-1 create iamserviceaccount — name alb-ingress-controller — namespace kube-system — override-existing-serviceaccounts — approve — cluster eks-alb-testing — attach-policy-arn arn:aws:iam::534***385:policy/ALBIngressControllerIAMPolicy
[ℹ] eksctl version 0.15.0
[ℹ] using region eu-north-1
[ℹ] 1 task: { 2 sequential sub-tasks: { create IAM role for serviceaccount “kube-system/alb-ingress-controller”, create serviceaccount “kube-system/alb-ingress-controller” } }
[ℹ] building iamserviceaccount stack “eksctl-eks-alb-testing-addon-iamserviceaccount-kube-system-alb-ingress-controller”
[ℹ] deploying stack “eksctl-eks-alb-testing-addon-iamserviceaccount-kube-system-alb-ingress-controller”
[ℹ] created serviceaccount “kube-system/alb-ingress-controller”Wait for its provision:
ALB Ingress ServiceAccount
Create a ServiceAccount named alb-ingress-controller in the kube-system namespace, add ClusterRoleBinding and ClusterRole named alb-ingress-controller with access rules:
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-alb-ingress-controller/v1.1.4/docs/examples/rbac-role.yaml
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/alb-ingress-controller created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/alb-ingress-controller created
serviceaccount/alb-ingress-controller createdCheck:
$ kubectl -n kube-system get serviceaccounts | grep alb
alb-ingress-controller 1 32sStart ALB Ingress Controller
We can launch it using the deployment file from here — https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-alb-ingress-controller/v1.1.4/docs/examples/alb-ingress-controller.yaml, which will spin up a pod using the docker.io/amazon/aws-alb-ingress-controller Docker image.
Clone it to your workstation:
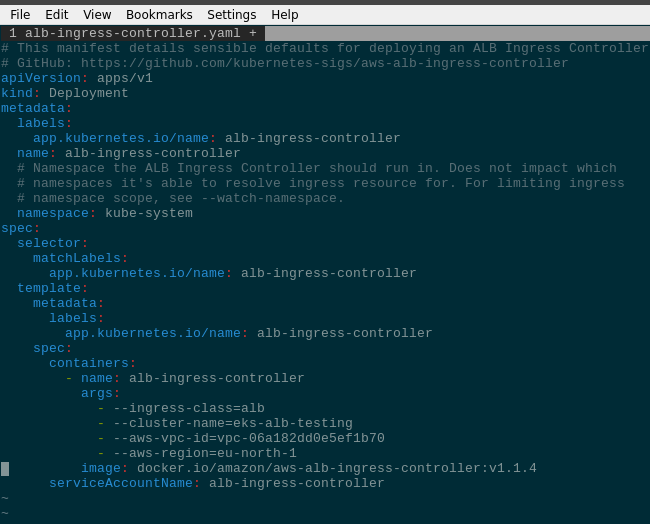
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-alb-ingress-controller/v1.1.4/docs/examples/alb-ingress-controller.yamlOpen for edit and in the block:
...
spec:
containers:
- name: alb-ingress-controller
args:
...Add the following arguments:
--cluster-name=eks-alb-testing--aws-vpc-id=vpc-06a182dd0e5ef1b70--aws-region=eu-north-1
VPC ID can be found in the Outputs of the root stack — eksctl-eks-alb-testing-cluster (check the AWS: CloudFormation — Nested Stacks and stacks parameters Import/Export post about how those stacks were created):
So the file has to look like the next:
Apply it to run ALB Ingress Controller:
$ kubectl apply -f alb-ingress-controller.yaml
deployment.apps/alb-ingress-controller createdCheck its pod:
$ kubectl -n kube-system get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
alb-ingress-controller-c47448d84–49tsc 1/1 Running 0 36sAnd the controller’s logs:
$ kubectl logs -n kube-system deployment.apps/alb-ingress-controller -f
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — -
AWS ALB Ingress controller
Release: v1.1.4
…
I0325 14:18:03.203499 1 leaderelection.go:205] attempting to acquire leader lease kube-system/ingress-controller-leader-alb…
I0325 14:18:03.211928 1 leaderelection.go:214] successfully acquired lease kube-system/ingress-controller-leader-alb
I0325 14:18:03.312309 1 controller.go:134] kubebuilder/controller “level”=0 “msg”=”Starting Controller” “controller”=”alb-ingress-controller”
I0325 14:18:03.412486 1 controller.go:154] kubebuilder/controller “level”=0 “msg”=”Starting workers” “controller”=”alb-ingress-controller” “worker count”=1Well — it is started, looks like even works — nice!
But is it really working? Let’s test.
ALB Ingress controller Testing
For the test — let’s spin up an additional deployment which will run a pod with NGINX and the Kubernetes Ingress Service in front of it.
So, need to create:
Kubernetes deployment for pods
a
NodePortService to route traffic to podsand
Ingressobject with the internet-facing ALB annotation - this has to trigger our ALB Controller to create an AWS Application Load Balancer
Apply:
$ kubectl apply -f nginx-testing-app.yml
deployment.apps/eks-alb-testing-deployment created
service/eks-alb-testing-web-service created
ingress.extensions/eks-alb-testing-web-ingress createdCheck the controller logs:
E0325 14:24:06.627453 1 controller.go:217] kubebuilder/controller “msg”=”Reconciler error” “error”=”no object matching key \”default/eks-alb-testing-web-ingress\” in local store” “controller”=”alb-ingress-controller” “request”={“Namespace”:”default”,”Name”:”eks-alb-testing-web-ingress”}
I0325 14:24:09.257834 1 security_group.go:36] default/eks-alb-testing-web-ingress: creating securityGroup dbd770cc-default-eksalbtes-09fa:managed LoadBalancer securityGroup by ALB Ingress Controller
…
I0325 14:24:09.665207 1 loadbalancer.go:191] default/eks-alb-testing-web-ingress: creating LoadBalancer dbd770cc-default-eksalbtes-09fa
…
I0325 14:24:10.636180 1 targets.go:80] default/eks-alb-testing-web-ingress: Adding targets to arn:aws:elasticloadbalancing:eu-north-1:534***385:targetgroup/dbd770cc-fe1e32fc96596dcf2c1/ef783b9fead58965: i-0622ff000570f32c7:31095, i-062329ba6419ba845:31095
I0325 14:24:10.821148 1 listener.go:110] default/eks-alb-testing-web-ingress: creating listener 80
…
I0325 14:24:13.171590 1 rules.go:82] default/eks-alb-testing-web-ingress: modifying rule 1 on arn:aws:elasticloadbalancing:eu-north-1:534***385:listener/app/dbd770cc-default-eksalbtes-09fa/979c262ea2e12983/455a07658116adcd
I0325 14:24:13.192456 1 rules.go:98] default/eks-alb-testing-web-ingress: rule 1 modified with conditions [{ Field: “path-pattern”, Values: [“/*”] }]Check Ingress resources:
$ kubectl get ingress -o wide
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
eks-alb-testing-web-ingress * dbd770cc-default-eksalbtes-09fa-1532296804.eu-north-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80 114sAnd try to connect to it:
$ curl -I dbd770cc-default-eksalbtes-09fa-1532296804.eu-north-1.elb.amazonaws.com
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Wed, 25 Mar 2020 14:26:27 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 612
Connection: keep-alive
Server: nginx/1.17.9
Last-Modified: Tue, 03 Mar 2020 14:32:47 GMT
ETag: “5e5e6a8f-264”
Accept-Ranges: bytesDone.
Originally published at RTFM: Linux, DevOps and system administration.
![RTFM! DevOps[at]UA](https://substackcdn.com/image/fetch/$s_!ruIs!,w_80,h_80,c_fill,f_auto,q_auto:good,fl_progressive:steep,g_auto/https%3A%2F%2Fsubstack-post-media.s3.amazonaws.com%2Fpublic%2Fimages%2F78e47926-bd0f-4929-a081-2588cc2a3d82_90x95.jpeg)

![RTFM! DevOps[at]UA](https://substackcdn.com/image/fetch/$s_!ruIs!,w_36,h_36,c_fill,f_auto,q_auto:good,fl_progressive:steep,g_auto/https%3A%2F%2Fsubstack-post-media.s3.amazonaws.com%2Fpublic%2Fimages%2F78e47926-bd0f-4929-a081-2588cc2a3d82_90x95.jpeg)